Advanced JavaScript With Google Tag Manager (GTM): A Practical Guide for Tracking & Analytics
Modern conversion tracking and analytics implementations require more than just basic tag firing. To build accurate, scalable, and future-proof tracking systems, advanced JavaScript knowledge inside Google Tag Manager is essential.
This guide explains core JavaScript concepts and shows how they are practically applied in GTM for GA4, Facebook (Meta), and other marketing platforms.
Why Advanced JavaScript Is Critical in Google Tag Manager
Google Tag Manager is not just a tag deployment tool—it is a JavaScript execution environment. Almost every advanced tracking requirement depends on:
- Custom JavaScript Variables
- DOM manipulation
- Dynamic data extraction
- dataLayer event architecture
- Schema-based data transformation
Understanding JavaScript allows you to:
- Track dynamic form values
- Capture user behavior accurately
- Maintain clean GA4 and Facebook event schemas
Avoid dependency on developers
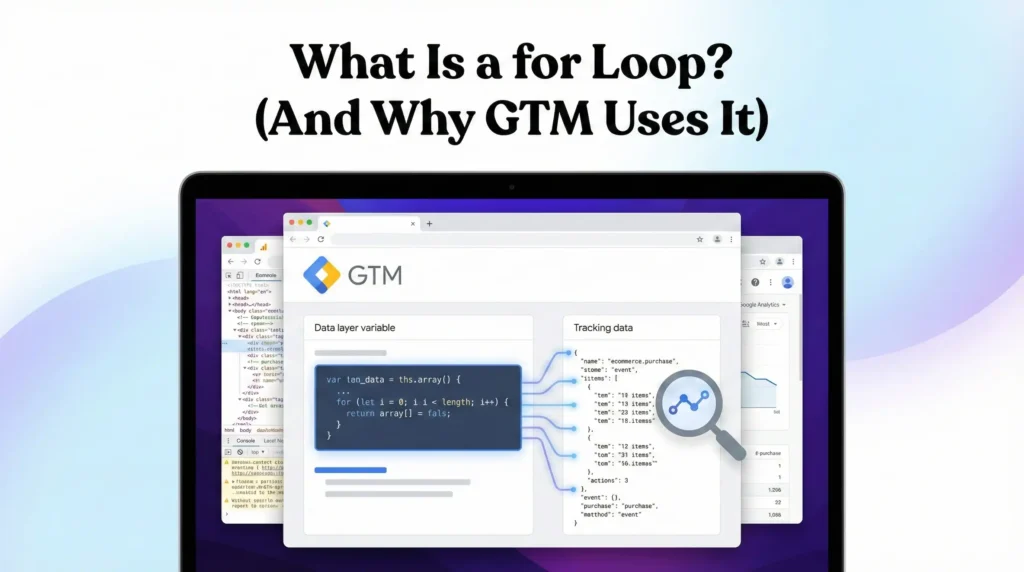
What Is a for Loop? (And Why GTM Uses It)
A for loop is used to iterate over arrays or collections of elements.
GTM Use Case
- Loop through multiple form fields
- Scan DOM elements (buttons, inputs, links)
- Extract values dynamically
Example Use Case
- Find a specific input field from multiple inputs
Loop through ecommerce items before pushing to dataLayer
What Is an if…else Statement?
An if–else statement controls logic flow based on conditions.
GTM Use Case
- Fire different events based on page type
- Send different parameters if a value exists or not
- Prevent duplicate event firing
Example
- If form submission is successful → push lead_submit
Else → do nothing
JavaScript Variables Explained (GTM Context)
JavaScript variables store values such as:
- Text
- Numbers
- Boolean values
- Objects
- Arrays
GTM-Specific Importance
- Custom JavaScript Variables rely entirely on variables
- Used to store DOM values, cookies, URL parameters, and localStorage data
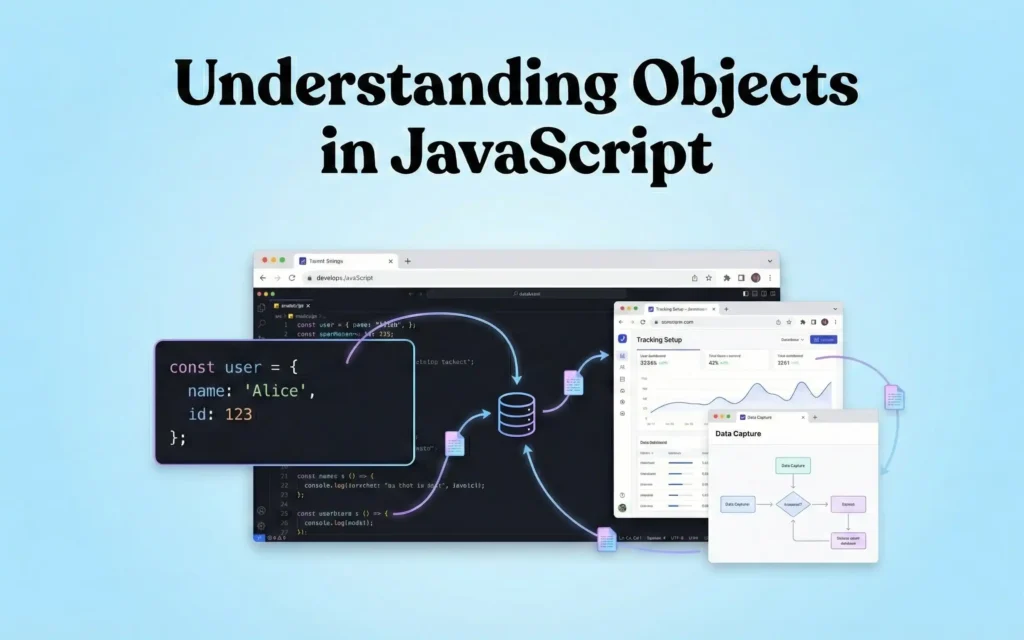
Understanding Objects in JavaScript
An object stores data in key–value pairs.
Example
{
event: "purchase",
value: 120,
currency: "USD"
}
GTM Use Case
- GA4 event parameters
- Facebook event payloads
- Ecommerce data models
Objects are the foundation of the dataLayer.
Understanding Arrays in JavaScript
An array stores multiple values in a list format.
GTM Use Case
- Product lists
- Multiple form fields
- Event parameter collections
Arrays are often nested inside objects when sending data to GA4 or Facebook.
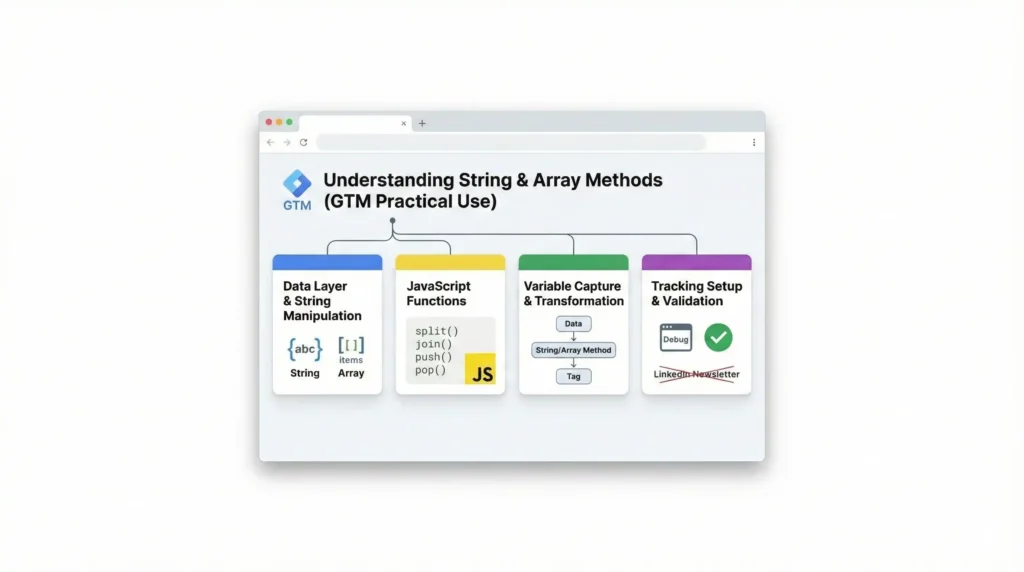
Understanding String & Array Methods (GTM Practical Use)
Common String Methods
- trim() – Clean whitespace
- toLowerCase() – Normalize values
- replace() – Format event names
Common Array Methods
- map() – Transform data structure
- filter() – Remove unwanted items
- forEach() – Loop through values
These methods are essential when aligning data with GA4 or Facebook schemas.
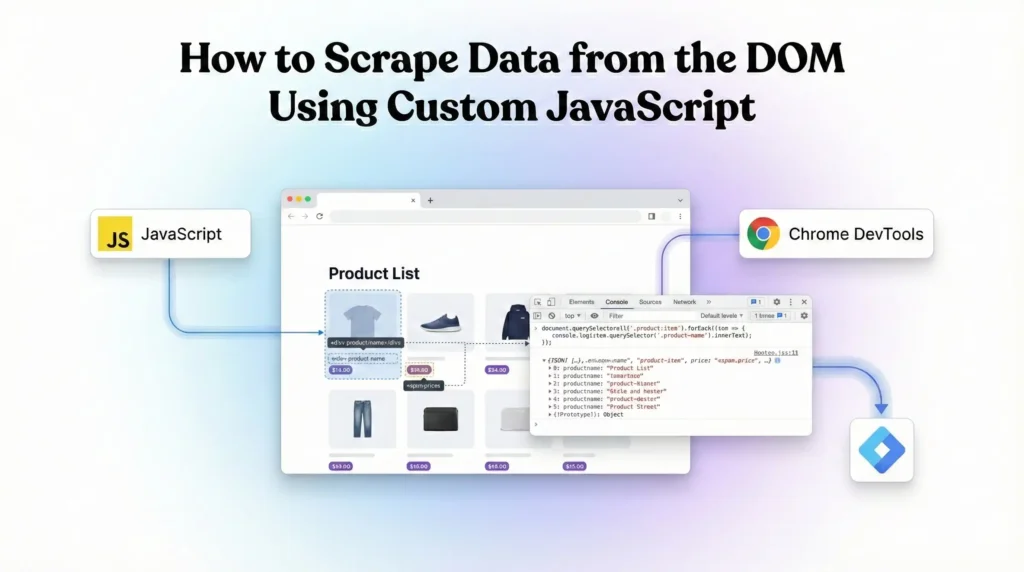
How to Scrape Data from the DOM Using Custom JavaScript
DOM scraping means extracting values directly from the webpage.
GTM Use Cases
- Capture form input values
- Read button text
- Extract dynamic pricing or IDs
Common Targets
- input fields
- select dropdowns
- Hidden fields
- Dynamic confirmation messages
This is commonly done using Custom JavaScript Variables in GTM.
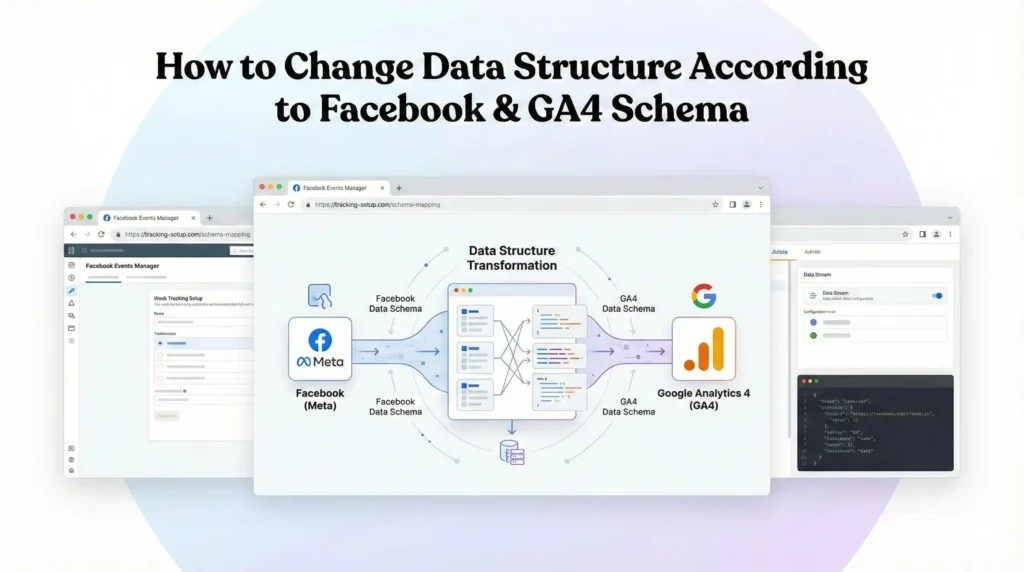
How to Change Data Structure According to Facebook & GA4 Schema
GA4 and Facebook require strict event structures.
Example
- GA4 requires flat event parameters
- Facebook requires nested objects like contents, value, currency
JavaScript is used to:
- Rename keys
- Rebuild objects
- Convert arrays
- Remove unsupported parameters
This ensures data accuracy and platform compliance.
How to Push Events into the dataLayer with Dynamic Parameters
Dynamic dataLayer pushes allow scalable tracking.
GTM Use Case
- Form submissions
- Button clicks
- Ecommerce events
- User engagement tracking
Each event can include:
- Event name
- Dynamic values
- Page-level context
User interaction details

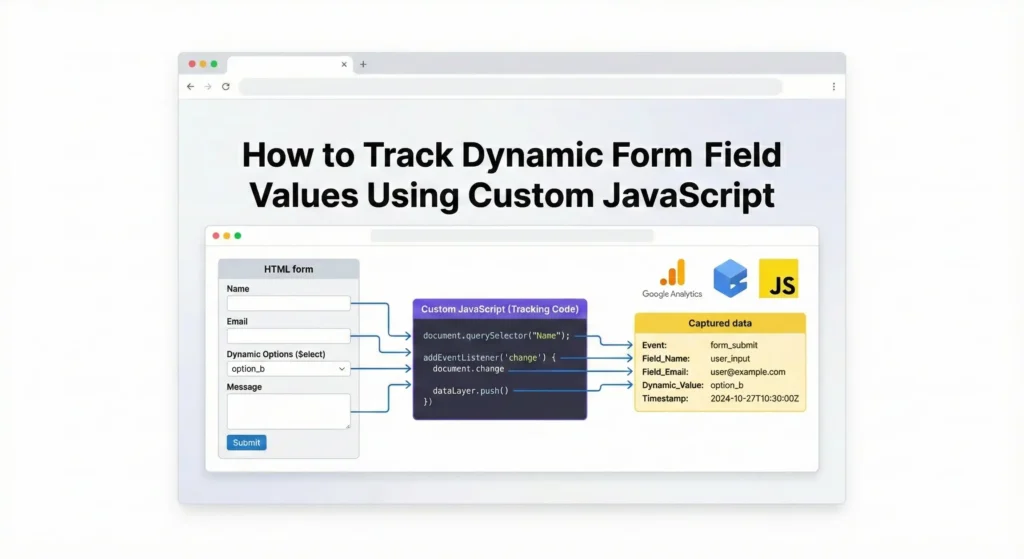
How to Track Dynamic Form Field Values Using Custom JavaScript
Many forms do not expose values directly to GTM.
Solution
- Use JavaScript to locate fields
- Read values on submission
- Push them dynamically to the dataLayer
This is critical for:
- Lead tracking
- CRM integrations
- GA4 enhanced reporting
How to Pass Dynamic Values Using Page URL Parameters
URL parameters are a common data carrier.
GTM Use Case
- Pass lead ID
- Campaign data
- User selections between pages
JavaScript allows GTM to:
- Read query parameters
- Store them
Reuse them later

How to Pass Dynamic Values Using localStorage
localStorage allows persistent data storage across pages.
GTM Use Case
- Store form values
- Persist user selections
- Pass data between multi-step forms
JavaScript makes it possible to:
- Set values
- Retrieve values
Clear values when needed

How to Listen to Any DOM Event Using Custom JavaScript
Some interactions are not supported by native GTM triggers.
Examples
- Third-party widgets
- SPA interactions
- Custom JS events
- AJAX-based submissions
JavaScript event listeners allow GTM to:
- Detect real user actions
- Trigger precise events
- Avoid false positives

Final Thoughts: Why This Matters for Modern Tracking
Advanced JavaScript with Google Tag Manager enables:
- Accurate GA4 event tracking
- Reliable Facebook conversion tracking
- Clean dataLayer architecture
- Future-proof analytics implementations
If you work with GA4, Google Ads, Facebook CAPI, ecommerce tracking, or lead generation, mastering these concepts is no longer optional—it is a core professional skill.
Troubleshooting & Common Mistakes
1. Tag Not Firing
- Cause: Typo in the Event Name.
- Fix: Check the Data Layer code (purchase_event) and the GTM Trigger (purchase_event). They must be identical (case-sensitive).
2. Duplicate Conversions
- Cause: User reloads the Thank You page.
- Fix: Ensure you mapped the Transaction ID in the Google Ads tag (Step 5.2). Google Ads automatically de-duplicates conversions with the same ID.
3. Missing Revenue Data
- Cause: The Variable {{dlv – value}} is reading undefined.
- Fix: Check the Data Layer structure. If your code pushes ecommerce.value but your variable looks for just value, it will fail. Ensure the dot notation matches the object structure perfectly.
4. Consent Mode Blocking Tags
- Cause: Tags fire before consent is granted.
- Fix: Ensure the Cookiebot tag uses the Consent Initialization trigger. Ensure all other tags wait for the specific event (like purchase_event) which happens after the page loads and consent is (usually) established.
5. Enhanced Conversions Error
- Cause: Email is not hashed or formatted correctly.
- Fix: GTM handles hashing automatically if you use the “User-provided Data” variable. Do not hash it manually in the Liquid code unless you aren’t using the GTM variable. Ensure the email is a raw string.
Conclusion
By implementing Advanced JavaScript and Data Layer tracking in Google Tag Manager, you have moved your analytics from a “guessing game” to a precision science. You are no longer reliant on basic page views. You are now tracking the actual engine of your website—the code that processes orders and forms.
This setup ensures that:
- Google Ads receives accurate, high-quality data to optimize your bidding.
- Consent Mode V2 keeps you compliant while recovering lost data through modeling.
- Enhanced Conversions future-proofs your tracking against cookie loss.
Do not let technical complexity scare you. Follow these steps, test rigorously, and you will build a data foundation that gives you a massive competitive advantage.
1. Why do I need JavaScript if GTM has built-in triggers?
Built-in triggers like “Form Submission” rely on standard HTML behavior. Modern websites often use custom scripts (AJAX) to handle forms, which bypasses standard HTML submission. Without custom JavaScript listeners, GTM simply doesn’t know the form was submitted.
2. Is this setup compliant with GDPR?
Yes, provided you use the Cookiebot integration as described. The logic ensures that if a user says “No” to cookies, the tags either don’t fire or fire in “Consent Mode” (pings only), which is the standard for compliance.
3. Can I use this for Facebook/Meta Pixel too?
Absolutely. The Data Layer is platform-agnostic. Once the data (Price, Order ID, Email) is in the Data Layer, you can use the exact same Variables and Triggers to fire a Facebook Purchase tag.
4. What happens if I don't use Enhanced Conversions?
You will lose attribution data. If a user clicks an ad on an iPhone (Safari) and buys the product 2 days later, standard cookies might be deleted by ITP (Intelligent Tracking Prevention). Enhanced Conversions can match that user via their email address, saving the conversion attribution.
5. Will this code slow down my website?
The GTM Listener code is extremely lightweight and runs asynchronously. It will not have a noticeable impact on your site speed. The Data Layer push on the Thank You page only runs once per order, so it has zero impact on browsing speed.
6. How do I test if Enhanced Conversions is working?
It takes up to 48 hours for the status to update in Google Ads. However, you can verify it immediately in GTM Preview Mode by checking if the “User-provided Data” variable contains the email address when the tag fires.
7. Do I need a developer to do this?
While having a developer helps, this guide provides the exact code snippets you need. If you are comfortable copying and pasting into Shopify’s settings and GTM, you can do this yourself.
8. Why is my Transaction ID variable undefined?
This usually happens because of nesting. If your Data Layer looks like ecommerce: { purchase: { actionField: { id: ‘123’ } } }, your variable name must be ecommerce.purchase.actionField.id. If you just put id, GTM won’t find it.
9. What is the difference between Data Layer and DOM?
The DOM is the visible HTML structure of your page. The Data Layer is an invisible JavaScript object specifically meant for data. Scraping the DOM is fragile (if you change your website design, tracking breaks). The Data Layer is robust and stable.
10. Can I track refunds with this?
Not with this specific client-side setup. Refunds happen on the backend (server). To track refunds, you would need to implement Offline Conversion Imports or Server-Side tracking, which connects directly to your CRM or Shopify API.


 Need Help Advanced Tracking Setup?
Need Help Advanced Tracking Setup?